Data is your business’s most powerful tool—but only if managed correctly. For SMEs in the financial sector, simply collecting data isn’t enough. Data can lead to confusion, missed opportunities, and compliance issues without effective governance. However, when managed strategically, data becomes the backbone of successful analytics, turning raw information into actionable insights. With the proper data governance, you’re not just organizing numbers—you’re enabling analytics that drive more intelligent decisions, uncover new growth opportunities, and give your business a competitive edge.
The Cost of Poor Data Management and Its Impact on Analytics
Despite the clear benefits, many SMEs struggle with the repercussions of poor data handling. Inconsistent data, for example, can lead to inaccurate analytics and misguided business decisions. When data is fragmented or conflicting across systems, it becomes difficult to generate reliable insights, leading to missed opportunities or misallocated resources. The following table outlines critical data management issues and their impacts on business operations:
| Data Management Issue | Impact on Analytics |
| Inconsistent Data | Leads to inaccurate analytics, resulting in flawed insights and misguided business decisions. |
| Lack of Governance | Inadequate data governance undermines the reliability of analytics and increases compliance risks. |
| Poor Data Quality | Results in unreliable analytics cause decisions based on flawed or incomplete information. |
| Operational Inefficiency | Ineffective data management causes delays and inefficiencies, hindering timely data-driven decision-making. |
| Difficulty in Data-Driven Decisions | Poor data management complicates the decision-making process, reducing confidence in the insights derived from analytics. |
| Compliance and Regulatory Risks | Inadequate data governance exposes SMEs to significant compliance and regulatory risks, which can lead to legal penalties and loss of trust. |
Effective Data Governance Practices: The Pillars of Strong Analytics
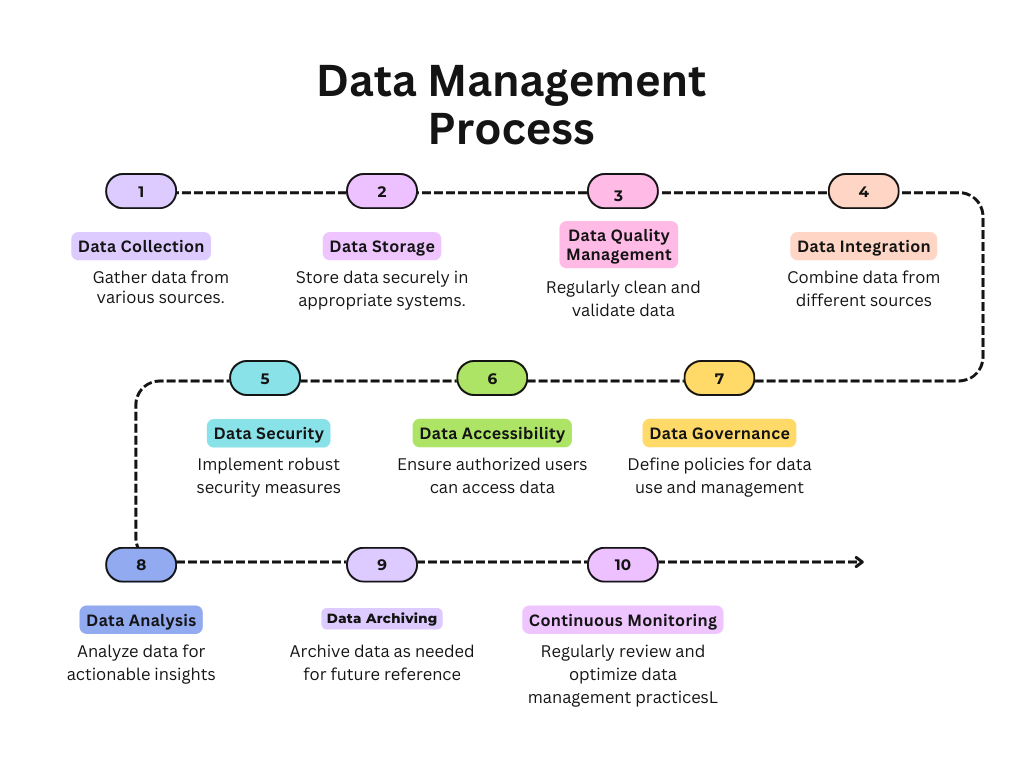
To overcome the challenges of poor data management, SMEs must focus on implementing effective data management practices. These key pillars ensure that data is well-organized, secure, and accessible, ultimately supporting better analytics and business outcomes:
Data Collection
- Purpose: Gathering data from various sources such as databases, external systems, and manual inputs.
- Key Activities: Ensuring data is collected systematically, in standardized formats, and from reliable sources.
Data Storage
- Purpose: Safely storing data in databases, data lakes, or cloud storage systems.
- Key Activities: Organizing data in a structured manner, ensuring scalability, and selecting the appropriate storage technology.
Data Quality Management
- Purpose: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Key Activities: Regularly cleaning data to remove duplicates, errors, and inconsistencies. Implementing validation rules and checks.
Data Integration
- Purpose: Combining data from different sources to provide a unified view.
- Key Activities: Using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, data warehousing, and ensuring that integrated data is consistent and accessible.
Data Security
- Purpose: Protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss.
- Key Activities: Implementing encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Data Accessibility
- Purpose: Making data easily accessible to authorized users.
- Key Activities: Implementing user-friendly data retrieval systems, ensuring proper indexing, and maintaining up-to-date data catalogs.
Data Governance
- Purpose: Establishing policies and procedures for data management across the organization.
- Key Activities: Defining data ownership, setting data usage policies, and ensuring compliance with data-related regulations.
Data Analysis and Reporting
- Purpose: Analyzing data to extract insights and generate reports for decision-making.
- Key Activities: Utilizing BI tools, dashboards, and advanced analytics techniques to provide actionable insights.
Data Archiving and Disposal
- Purpose: Managing the data lifecycle, including its eventual archiving or secure disposal.
- Key Activities: Archiving data that is no longer in active use but may be needed in the future and securely deleting obsolete or no longer required data.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Purpose: Ensuring ongoing optimization of data management practices.
- Key Activities: Regularly reviewing and updating data management policies, monitoring data quality, and incorporating feedback for improvements.
Future-Proofing Your Business with Insight Expertise
As businesses evolve, so must their data management practices. Effective data management enhances analytics capabilities and prepares SMEs for future growth and challenges. By ensuring data is well-organized and accessible, businesses can scale their analytics efforts with growth, maintaining competitiveness in a dynamic market. Additionally, robust data management provides the flexibility to adapt quickly to changing conditions, helping businesses stay agile and responsive to new opportunities.
Insight Consultants’ data strategy guidance service plays a vital role in this transformation. We help companies develop and implement a comprehensive data strategy that aligns with their operational needs. Our expertise includes developing a cohesive data architecture, implementing best practices in data governance, and facilitating seamless integration. Additionally, we provide specialized services in business intelligence, supply chain analytics, risk analytics, and decision modeling to enhance operational efficiency and support informed decision-making.
Contact us to learn how we can help you implement robust data governance, which can transform your analytics and future-proof your business.







